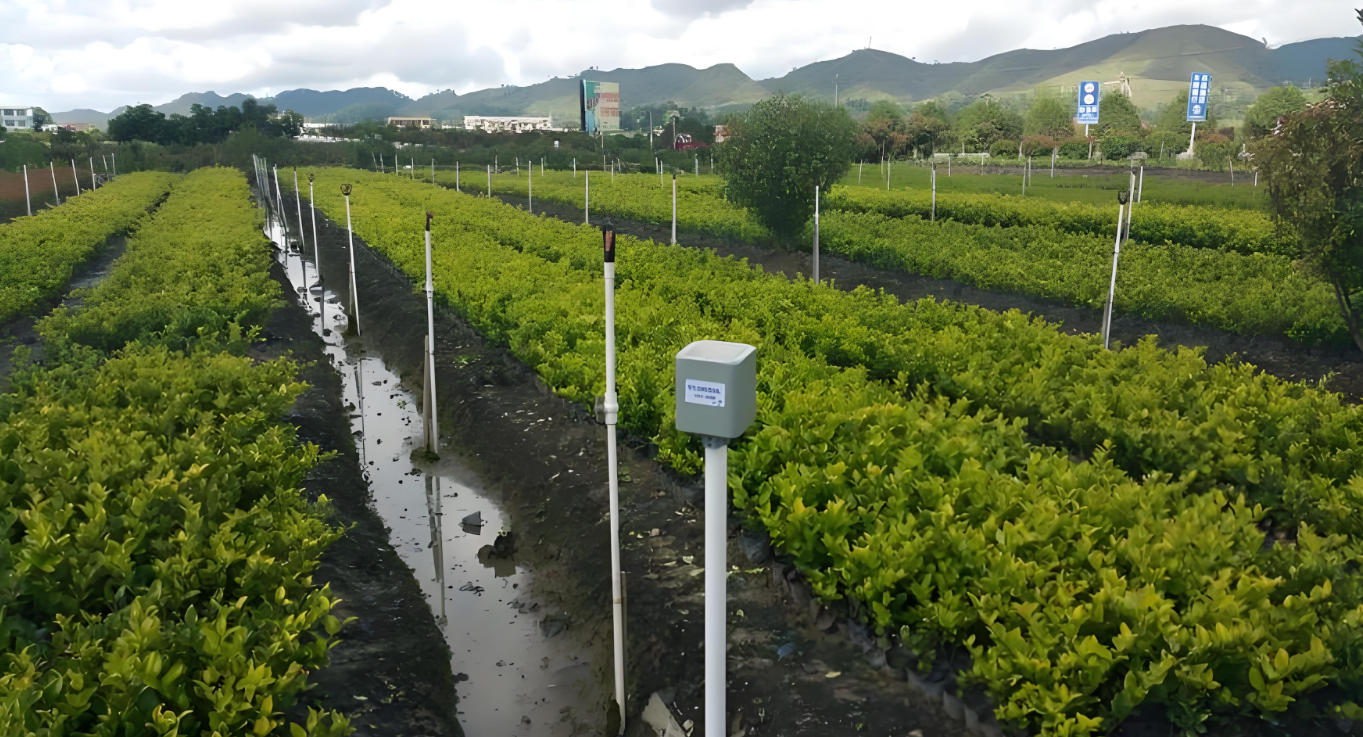
The smart agriculture irrigation industry experienced significant advancements in 2016, driven by the increasing need for water conservation, precision farming, and the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies. With global concerns over water scarcity and the growing demand for sustainable agricultural practices, smart irrigation systems gained traction among farmers, agribusinesses, and governments.
Market Growth and Key Drivers
1. Government Support and Subsidies
Governments and international organizations promoted smart irrigation to enhance agricultural productivity while conserving water. Key initiatives included:
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) provided funding for precision agriculture technologies under programs like the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP).
The European Union supported smart farming projects through its Horizon 2020 research program.
Countries like India and Israel introduced subsidies for drip irrigation and sensor-based systems to reduce water waste.
2. Advancements in IoT and Sensor Technology
2016 saw rapid improvements in IoT-enabled irrigation systems. Key technological developments included:
Soil moisture sensors that provided real-time data to prevent over- or under-watering.
Weather-based irrigation controllers (WBICs) that adjusted watering schedules based on forecasts.
Drones and satellite imaging for monitoring crop health and irrigation needs across large farms.
3. Increasing Adoption of Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture, which relies on data-driven farming techniques, became more widespread in 2016.
Improve crop yields through optimized irrigation scheduling.
Lower energy costs by reducing pump usage.
Challenges Facing the Industry
Despite its growth, the smart irrigation industry faced several challenges in 2016:
1. High Initial Costs
The upfront investment for smart irrigation systems (sensors, controllers, software) was a barrier for small-scale farmers, particularly in developing countries. However, long-term savings in water and energy costs helped justify the expense.
2. Lack of Technical Knowledge
Many farmers, especially in rural areas, lacked the expertise to operate advanced irrigation technologies. Companies and governments addressed this through training programs and user-friendly interfaces.
3. Connectivity Issues in Remote Areas
IoT-based irrigation systems required reliable internet or cellular connectivity, which was limited in some agricultural regions. Solutions such as low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) and LoRaWAN began emerging to improve connectivity.
4. Data Security Concerns
As farming became more data-dependent, cybersecurity risks increased. Farmers and agribusinesses needed secure cloud platforms to protect sensitive irrigation and crop data.
Regional Market Trends
North America
The U.S. and Canada led in smart irrigation adoption, driven by:
Severe droughts in California, prompting investments in smart drip irrigation.
Europe
European countries focused on sustainability, with:
Israel remaining a global leader in drip irrigation technology.
Spain and Italy implementing smart water management policies for vineyards and olive farms.
Asia-Pacific
India saw growth due to government schemes like Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY), promoting micro-irrigation.
China invested heavily in smart agriculture, integrating AI and IoT into irrigation systems.
Latin America and Africa
Brazil adopted smart irrigation for sugarcane and soybean farms.
South Africa and Kenya piloted solar-powered irrigation projects to combat water shortages.
Key Companies and Innovations in 2016
Netafim (Israel) – Expanded its drip irrigation and IoT-based solutions for large-scale farms.
Baseline Inc. (U.S.) – Launched advanced cloud-based irrigation control systems.
Hortau (Canada) – Introduced wireless soil tension sensors for real-time irrigation management.
CropX (Israel/U.S.) – Developed AI-driven irrigation software to optimize water use.
Future Outlook
The smart irrigation industry was poised for exponential growth beyond 2016, with emerging trends such as:
Solar-powered smart irrigation systems for off-grid farming.
Integration with autonomous farming equipment (e.g., self-driving tractors with irrigation capabilities).
Conclusion
2016 was a transformative year for the smart agriculture irrigation industry, marked by technological innovation, increased adoption, and strong government support. While challenges like high costs and connectivity issues persisted, the long-term benefits of water conservation, improved crop yields, and sustainability ensured continued growth. With advancements in IoT, AI, and renewable energy, smart irrigation was set to revolutionize global agriculture in the coming years.